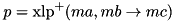|
YAARX: Yet Another ARX Toolkit
0.1
|
 |
YAARX: Yet Another ARX Toolkit
0.1
|
The XOR linear probability of ADD 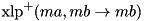 .
More...
.
More...
Functions | |
| double | xlp_add_exper (const WORD_T ma, const WORD_T mb, const WORD_T mc, const WORD_T word_size) |
| double | xlc_add_nopt (const WORD_T ma, const WORD_T mb, const WORD_T mc, const WORD_T word_size) |
| int | xlc_add_sign (const WORD_T ma, const WORD_T mb, const WORD_T mc, const WORD_T word_size) |
| double | xlp_add (const WORD_T ma, const WORD_T mb, const WORD_T mc, const WORD_T word_size) |
| double | xlb_add (const WORD_T ma, const WORD_T mb, const WORD_T mc, const WORD_T word_size) |
The XOR linear probability of ADD 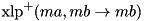 .
.
| double xlb_add | ( | const WORD_T | ma, |
| const WORD_T | mb, | ||
| const WORD_T | mc, | ||
| const WORD_T | word_size | ||
| ) |
Compute the bias of the following linear approximation of modular addition:
(a . ma) ^ (b . mb) = (c . mc)
where (x . ma) denotes the dot product between the word x and the mask mx.
xlb is computed from xlp using the relation:
xlb = xlp - 1/2
| ma | first input mask. |
| mb | second input mask. |
| mc | output mask. |
| word_size | word size in bits |
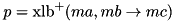
| double xlc_add_nopt | ( | const WORD_T | ma, |
| const WORD_T | mb, | ||
| const WORD_T | mc, | ||
| const WORD_T | word_size | ||
| ) |
The absolute XOR linear correlation of ADD ( 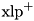 ) Complexity:
) Complexity: 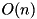 .
.
XCP is the correlation of the following linear approximation of modular addition, computed over the inputs a and b
(a . ma) ^ (b . mb) = (c . mc)
where (x . ma) denotes the dot product between the word x and the mask mx.
| ma | first input mask. |
| mb | second input mask. |
| mc | output mask. |
| word_size | word size in bits |
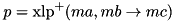
bias = prob - 1/2 corr = (2 * bias) = (2 * prob) - 1
xlc_add is an optimized version
Non-optimized version
if at state 0 halt (probability = 1/2, bias = 0)
if at state 0 halt (probability = 1/2, bias = 0)
| int xlc_add_sign | ( | const WORD_T | ma, |
| const WORD_T | mb, | ||
| const WORD_T | mc, | ||
| const WORD_T | word_size | ||
| ) |
Compute the sign of the XOR linear correlation of ADD ( 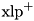 )
)
| ma | first input mask. |
| mb | second input mask. |
| mc | output mask. |
| word_size | word size in bits |
| double xlp_add | ( | const WORD_T | ma, |
| const WORD_T | mb, | ||
| const WORD_T | mc, | ||
| const WORD_T | word_size | ||
| ) |
The XOR linear probability of ADD ( 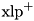 ) Complexity:
) Complexity: 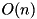 .
.
XLP is the probability over the inputs a and b that the following equation holds:
(a . ma) ^ (b . mb) = (c . mc)
where (x . ma) denotes the dot product between the word x and the mask mx.
xlp is computed from xlc using the relation:
xlc = (2 * xlp) - 1
together with the fact that the sign of xlc is -1 iff HW((ma ^ mc) & (mb ^ mc)) is odd.
| ma | first input mask. |
| mb | second input mask. |
| mc | output mask. |
| word_size | word size in bits |
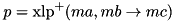
| double xlp_add_exper | ( | const WORD_T | ma, |
| const WORD_T | mb, | ||
| const WORD_T | mc, | ||
| const WORD_T | word_size | ||
| ) |
The XOR linear probability of ADD ( 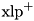 ) computed experimentally over all inputs. Complexity:
) computed experimentally over all inputs. Complexity: 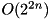 .
.
XLP is the probability over the inputs a and b that the following equation holds:
(a . ma) ^ (b . mb) = (c . mc)
where (x . ma) denotes the dot product between the word x and the mask mx.
| ma | first input mask. |
| mb | second input mask. |
| mc | output mask. |
| word_size | word size in bits |