 |
YAARX: Yet Another ARX Toolkit
0.1
|
 |
YAARX: Yet Another ARX Toolkit
0.1
|
Analysis of block cipher Salsa20. More...
Functions | |
| double | xdp_add_dset_salsa_arx (gsl_matrix *A[3][3][3], diff_set_t dx, diff_set_t dy, diff_set_t dz, diff_set_t *dt, uint32_t k, bool b_single_diff) |
| double | xdp_add_dset_salsa20 (const uint32_t e[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5], const uint32_t r_start, const uint32_t r_end, gsl_matrix *A[3][3][3], const diff_set_t DX_in[SALSA_STATE], diff_set_t DY_in[SALSA_STATE], diff_set_t DT[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE], double P[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE]) |
| double | xdp_add_dset_salsa20_exper (const uint32_t e[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5], const uint32_t r_start, const uint32_t r_end, uint32_t npairs, const diff_set_t DX_set[SALSA_STATE], diff_set_t DY_set[SALSA_STATE], double PW[SALSA_STATE]) |
| uint32_t | salsa_arx (uint32_t x, uint32_t y, uint32_t z, uint32_t k) |
| void | salsa20 (const uint32_t e[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5], const uint32_t r_start, const uint32_t r_end, const uint32_t X_in[SALSA_STATE], uint32_t Y_in[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_sigma_to_uint32 (uint32_t X[4], const char c[17]) |
| void | salsa_gen_rand_input_state (uint32_t X[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_print_state_uint32 (const uint32_t X[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_print_state_uint8 (const uint8_t X[4 *SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_uint8_to_uint32 (const uint8_t X[4], uint32_t *Y) |
| void | salsa_uint32_to_uint8 (uint8_t X[4], const uint32_t Y) |
| void | salsa_state_uint8_to_uint32 (const uint8_t X[4 *SALSA_STATE], uint32_t Y[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_state_uint32_to_uint8 (uint8_t X[4 *SALSA_STATE], const uint32_t Y[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_print_trail (uint32_t nrounds, diff_set_t DT[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE], double P[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_compute_prob_rand (const diff_set_t Y[SALSA_STATE], double P[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_print_prob (double P[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_print_prob_vs_rand (double P[SALSA_STATE], double P_rand[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_gen_rand_shift_const (uint32_t E[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5]) |
| void | salsa_gen_word_deps (const uint32_t nrounds, const uint32_t e[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5], uint32_t D[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_word_probs (const uint32_t nrounds, const uint32_t e[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5], double PT[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE], uint32_t D[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE], double P[SALSA_STATE]) |
| void | salsa_word_probs_v2 (const uint32_t r_start, const uint32_t r_end, const uint32_t e[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5], double PT[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE], double P[SALSA_STATE]) |
Variables | |
| const char | sigma [17] = "expand 32-byte k" |
| uint32_t | E [SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5] |
Analysis of block cipher Salsa20.
| uint32_t salsa_arx | ( | uint32_t | x, |
| uint32_t | y, | ||
| uint32_t | z, | ||
| uint32_t | k | ||
| ) |
The ARX primitive of Salsa20: t = z ^ ((x + y) <<< k);
| void salsa_compute_prob_rand | ( | const diff_set_t | Y[SALSA_STATE], |
| double | P[SALSA_STATE] | ||
| ) |
Compute the random case for the probability.
| void salsa_gen_rand_input_state | ( | uint32_t | X[SALSA_STATE] | ) |
Generate a random input state.
| void salsa_gen_rand_shift_const | ( | uint32_t | E[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5] | ) |
Generate random shift constants. Used when the word size is less than 32.
| void salsa_gen_word_deps | ( | const uint32_t | nrounds, |
| const uint32_t | e[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5], | ||
| uint32_t | D[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE] | ||
| ) |
Generate an array of dependencies of each of the SALSA_STATE number of output words after ROUNDS number of rounds upon some of the modular additions in rounds 0,1,2,...,ROUNDS-2. dep[i][j] are 32-bit words of which only the 16 lsb bits are used. each of these 16 bits corresponds to one modular addition in the given round.
Example: Let ROUNDS = 3. Then each of the 16 words after round 3 depends on some modular additions from rounds 1,2 and 3. Let's say that word 4 depends on additions 1 and 8 after round 1 (if we start counting from zero this is a 16-bit word with bits #1 and #8 set to 1: 0x0102), on additions 2 and 7 after round 2 (0x0044) and on additions 15 and 3 after round 3 (0x8010). Then the corresponding entry of dep for word 4 will be:
dep[4] = {0x0082, 0x0044, 0x8010}
The modular additions in a given round are enumerated with the same index as the index of the word which is computed by using this modular addition.
Example: The modular addition (word[0] + word[12]) described with the pair (word[0], word[12]) and used to compute word 4 has index 4:
word[4] = XOR(word[4],ROTATE(PLUS(word[0],word[12]), 7);
So the addition PLUS(word[0],word[12]) has index 4 in the dep array.
| void salsa_print_state_uint32 | ( | const uint32_t | X[SALSA_STATE] | ) |
Print state in 32-bit words.
| void salsa_print_state_uint8 | ( | const uint8_t | X[4 *SALSA_STATE] | ) |
Print state in 8-bit words.
| void salsa_sigma_to_uint32 | ( | uint32_t | X[4], |
| const char | c[17] | ||
| ) |
Convert the 16 Byte constant sigma of Salsa20 into an array of 4 32-bit words.
| void salsa_word_probs | ( | const uint32_t | nrounds, |
| const uint32_t | e[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5], | ||
| double | PT[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE], | ||
| uint32_t | D[MAX_NROUNDS][SALSA_STATE], | ||
| double | P[SALSA_STATE] | ||
| ) |
Given the probabilities for each of the words of the state after every round PT computed with xdp_add_dset_salsa20 , and the array of word dependencies D computed with salsa_gen_word_deps , compute the individual probabilities for each of the words of the state after nrounds .
P[0] is the initial input and therefore P[i] is the output from round 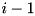 .
. | uint32_t E[SALSA_STATE+SALSA_STATE][5] |
The array e encodes the operations of the Salsa column round by providing the indexes of the words on which operations are performed. The information for i-th entry of e is interpreted as follow (see the column round operation of Salsa20):
e[i][0] = XOR( e[i][1], LROT( ADD(e[i][2],e[i][3]), e[i][4]) ) = e[i][1] ^ ((e[i][2] + e[i][3]) <<< e[i][4])
| const char sigma[17] = "expand 32-byte k" |
The constants c for 256-bit (32 Bytes) key.