 |
YAARX: Yet Another ARX Toolkit
0.1
|
 |
YAARX: Yet Another ARX Toolkit
0.1
|
Header file for rc5-eq.cc: Procedures for solving certain equations arising during the differential analysis of block cipher RC5 . One such equation is the following equation in x from the last round of RC5: . More...
Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | pair_t |
| struct | bits_t |
| struct | eq_x_params_t |
| struct | rc5_eq_x_params_equal_to |
| struct | rc5_eq_x_params_hash |
Macros | |
| #define | RC5_ADD_APPROX 0 |
| #define | RC5_LAST_ROUND_ADD_APPROX 0 |
| #define | RC5_LAST_ROUND_PARAMS_INCLUDE_DX 0 |
| #define | RC5_LAST_ROUND_PARAMS_NVARIANTS_CUT_THRES 5 |
| #define | RC5_ADD_APPROX_ORDER 5 |
| #define | RC5_ADD_APPROX_P_THRES 1.0 |
| #define | RC5_LAST_ROUND_NMATRIX 8 |
| #define | RC5_LAST_ROUND_MSIZE 4 /* Number of state values (s1, s2) */ |
| #define | RC5_LAST_ROUND_ISTATE 3 |
| #define | RC5_XDP_ADD_LAST_ROUND_COLSUM 2 |
| #define | RC5_XDP_ADD_LAST_ROUND_NORM 1.0 /(double)RC5_XDP_ADD_LAST_ROUND_COLSUM |
| #define | RC5_MID_ROUND_ISTATE 3 |
| #define | RC5_MID_ROUND_NMATRIX 4 |
| #define | RC5_MID_ROUND_MSIZE 4 /* Number of state values (s1, s2) */ |
| #define | RC5_XDP_ADD_MID_ROUND_COLSUM 4 |
| #define | RC5_XDP_ADD_MID_ROUND_NORM 1.0 /(double)RC5_XDP_ADD_MID_ROUND_COLSUM |
Functions | |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_alloc_matrices_3d (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_free_matrices_3d (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_alloc_matrices_4d (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_free_matrices_4d (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_print_matrices (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_print_matrices (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_add_matrices (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2], gsl_matrix *AA[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_normalize_matrices (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_key_sf (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2]) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_eq_key_is_contradicting (const gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2], const gsl_vector *L, const gsl_vector *C, const WORD_T y, const WORD_T yy, const WORD_T dx, double *nval) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_eq_key_check_conflict_exper (WORD_T y, WORD_T yy, WORD_T dx) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_key_detect_fixed_key_bits (const gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2], const gsl_matrix *AA[2][2][2][2], const gsl_vector *L, const gsl_vector *C, const WORD_T y, const WORD_T yy, const WORD_T dx) |
| bool | rc5_struct_eq_x_params_compare_by_nvariants (const eq_x_params_t first, const eq_x_params_t second) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_x_sf (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_last_round_eq_x_count_solutions_all_inputs (const gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2], const gsl_matrix *AA[2][2][2][2]) |
| uint32_t | rc5_last_round_eq_x_count_solutions_exper (uint32_t y, uint32_t yy, uint32_t dx, std::vector< uint32_t > *sol_vec) |
| double | rc5_xdp_add_last_round (const gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2], const gsl_vector *L, const gsl_vector *C, const WORD_T y, const WORD_T yy, const WORD_T dx) |
| void | rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out_exper (const WORD_T y, const WORD_T yy, const double p_thres, std::vector< WORD_T > *dx_vec) |
| void | rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out_wrapper (const WORD_T y, const WORD_T yy, const double p_thres, std::vector< WORD_T > *dx_vec) |
| void | rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out_i (const uint32_t i, const double p_thres, const uint32_t hw_thres, const gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2], const gsl_vector *L, const gsl_vector *C, const WORD_T y, const WORD_T yy, const WORD_T dx_prev, const uint32_t rot_const_prev, const WORD_T dx, const double p, std::vector< WORD_T > *dx_vec) |
| void | rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out (const gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2], const gsl_vector *L, const gsl_vector *C, const WORD_T y, const WORD_T yy, const WORD_T dx_prev, const uint32_t rot_const_prev, const double p_thres, const uint32_t hw_thres, std::vector< WORD_T > *dx_vec) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_eq_x_find_solutions_rec (const gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2], const eq_x_params_t eq_params, std::vector< WORD_T > *sol_vec) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_eq_x_has_solution (const uint32_t i, const gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2], const gsl_vector *L, const gsl_vector *C, const eq_x_params_t eq_params, const WORD_T x_sol, WORD_T *sol) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_eq_x_find_solutions_exper (WORD_T y, WORD_T yy, WORD_T dx, std::vector< WORD_T > *sol_vec) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_eq_x_is_solution (const WORD_T x, const WORD_T y, const WORD_T yy, const WORD_T dx) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_eq_x_bit_seq_match (const WORD_T x, const uint32_t rot_const, const WORD_T bit_seq, const uint32_t bit_seq_len) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_eq_x_bit_seq_match_bitwise (const WORD_T x, const uint32_t rot_const, const WORD_T bit_seq, const uint32_t bit_seq_len) |
| double | rc5_xdp_add_last_round_exper (WORD_T y, WORD_T yy, WORD_T dx) |
| double | rc5_xdp_add_last_round (uint32_t y, uint32_t yy, uint32_t dx) |
| bool | rc5_last_round_add_approx_match (const uint32_t i, const WORD_T x_in, const WORD_T xx_in, const WORD_T dy, const WORD_T dz, const uint32_t order_in) |
| double | rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_exper (const WORD_T dy, const WORD_T dx) |
| bool | rc5_mid_round_eq_xy_find_solutions_exper (const WORD_T dy, const WORD_T dx, std::vector< WORD_T > *sol_vec) |
| void | rc5_mid_round_eq_xy_sf (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_mid_round_eq_alloc_matrices_2d (gsl_matrix *A[2][2]) |
| void | rc5_mid_round_eq_free_matrices_2d (gsl_matrix *A[2][2]) |
| void | rc5_mid_round_eq_alloc_matrices_4d (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_mid_round_eq_free_matrices_4d (gsl_matrix *A[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_mid_round_eq_add_matrices (gsl_matrix *A[2][2], gsl_matrix *AA[2][2][2][2]) |
| void | rc5_mid_round_eq_normalize_matrices (gsl_matrix *A[2][2]) |
| void | rc5_mid_round_eq_print_matrices (gsl_matrix *A[2][2]) |
| double | rc5_xdp_add_mid_round (const gsl_matrix *A[2][2], const gsl_vector *L, const gsl_vector *C, const WORD_T dy, const WORD_T dx) |
| void | rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out_exper (const WORD_T dy, const double p_thres, std::vector< WORD_T > *dx_vec) |
| void | rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out (const gsl_matrix *A[2][2], const gsl_vector *L, const gsl_vector *C, const WORD_T dy, const WORD_T dx_prev, const uint32_t rot_const_prev, const double p_thres, const WORD_T hw_thres, std::vector< WORD_T > *dx_vec) |
| void | rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out (const WORD_T dy, const WORD_T dx_prev, const WORD_T rot_const_prev, const double p_thres, const uint32_t hw_thres, std::vector< WORD_T > *dx_vec) |
| bool | rc5_mid_round_add_approx_match (const uint32_t i, const WORD_T dx, const WORD_T dy, const WORD_T dz, const uint32_t order_in) |
| double | rc5_xdp_add_first_round_exper (WORD_T x, WORD_T xx, WORD_T dy) |
Header file for rc5-eq.cc: Procedures for solving certain equations arising during the differential analysis of block cipher RC5 . One such equation is the following equation in x from the last round of RC5: .
| #define RC5_ADD_APPROX_ORDER 5 |
By definition the order of the approximation of the modular addition is the number of bits of the input operands that are used in order to compute one bit of the output operand (i.e. the size of the sliding window in bits).
For example, an approximation of order 2 considers bits i and and i-1 of x and y in order to compute bit i of z where z = x (+*) y and +* denotes the order 2 approximation of addition:
z[i] = x[i] ^ y[i] ^ (x[i-1] & y[i-1].
It follows that XOR is an approximation of order 1.
Approximation of order 0 is equivalent to the original operation
| #define RC5_ADD_APPROX_P_THRES 1.0 |
Apply the ADD approximation only if the probability p_thres from RC5_P_THRES_ARRAY is below the threshold RC5_ADD_APPROX_P_THRES. If the latter is equal to 1.0 then the add approximation is applied always.
| #define RC5_LAST_ROUND_PARAMS_NVARIANTS_CUT_THRES 5 |
Take the top 5 suggestions for params strcuture, based on number of variants.
| #define RC5_XDP_ADD_LAST_ROUND_COLSUM 2 |
Sum of non-zero elements in one column.
| #define RC5_XDP_ADD_LAST_ROUND_NORM 1.0 /(double)RC5_XDP_ADD_LAST_ROUND_COLSUM |
Normalization factor for the matrices.
| #define RC5_XDP_ADD_MID_ROUND_COLSUM 4 |
Sum of non-zero elements in one column.
| #define RC5_XDP_ADD_MID_ROUND_NORM 1.0 /(double)RC5_XDP_ADD_MID_ROUND_COLSUM |
Normalization factor for the matrices.
| bool rc5_last_round_add_approx_match | ( | const uint32_t | i, |
| const WORD_T | x_in, | ||
| const WORD_T | xx_in, | ||
| const WORD_T | dy, | ||
| const WORD_T | dz, | ||
| const uint32_t | order_in | ||
| ) |
Consider an approximation of modular subtraction of order order. For fixed x, xx, and dy cycle over all possible 2^{order} values of y until we find at least one that satisfies the equation
((x -* y) ^ (xx -* (y ^ dy)))[i] = dz[i] ,
where -* denotes approximation of modular subtraction.
See xdp_sub_fixed_x_approx_rec
| void rc5_last_round_eq_alloc_matrices_4d | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2] | ) |
Allocate memory for the last round equation of RC5
| void rc5_last_round_eq_free_matrices_3d | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2] | ) |
Free memory reserved by a previous call to rc5_last_round_eq_alloc_matrices_3d .
| void rc5_last_round_eq_free_matrices_4d | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2] | ) |
Free memory reserved by a previous call to rc5_last_round_eq_alloc_matrices .
| void rc5_last_round_eq_key_detect_fixed_key_bits | ( | const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2], |
| const gsl_matrix * | AA[2][2][2][2], | ||
| const gsl_vector * | L, | ||
| const gsl_vector * | C, | ||
| const WORD_T | y, | ||
| const WORD_T | yy, | ||
| const WORD_T | dx | ||
| ) |
Detect bits of the key that are fixed by y, yy, dx A = AA[0] + AA[1], where AA[k[i]][y[i]][yy[i]][dx[i]] Note: no fixed key bits exist
| bool rc5_last_round_eq_key_is_contradicting | ( | const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2], |
| const gsl_vector * | L, | ||
| const gsl_vector * | C, | ||
| const WORD_T | y, | ||
| const WORD_T | yy, | ||
| const WORD_T | dx, | ||
| double * | nval | ||
| ) |
Detect contradictions in the key bits: k[i] != kk[i] for some i A = AA[0] + AA[1], where AA[k[i]][y[i]][yy[i]][dx[i]]
| void rc5_last_round_eq_key_sf | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2] | ) |
Construct the transition probability matrices for the S-function corresponding to the following equation from the last round: 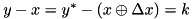
| A | ![$ A[k[i]][][][] $](form_299.png) : zero-initialized set of matrices corresponding resp. to : zero-initialized set of matrices corresponding resp. to ![$k[i] = kk[i] = 0$](form_300.png) and and ![$k[i] = kk[i] = 1$](form_301.png) . . |
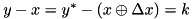
![$A[2][2][2][2] = A[k[i]][y[i]][y^{*}[i]][\Delta{x[i]}]$](form_302.png) , where
, where
![$y[i]$](form_303.png) : the i-th bit of the first output value.
: the i-th bit of the first output value.![$y^{*}[i]$](form_304.png) : the i-th bit of the second output value.
: the i-th bit of the second output value.![$\Delta{x[i]}$](form_305.png) : the i-th bit of the input difference.
: the i-th bit of the input difference. | void rc5_last_round_eq_print_matrices | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2] | ) |
Print the matrices for last round eq. of RC5.
| void rc5_last_round_eq_print_matrices | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2] | ) |
Print the matrices for last round eq. of RC5.
| bool rc5_last_round_eq_x_bit_seq_match | ( | const WORD_T | x, |
| const uint32_t | rot_const, | ||
| const WORD_T | bit_seq, | ||
| const uint32_t | bit_seq_len | ||
| ) |
Check if the following holds:
x[(rot_const + log2(w)) : rot_const] = (rot_const_prev ^ rot_const),
where
rot_const = (ciphertext_left[n] & RC5_ROT_MASK) rot_const_prev = (ciphertext_left[n-1] & RC5_ROT_MASK)
For example in the GoUp filter the rotation constants in the last two rounds are resp. r6 and r7 and are of size log2(w) bits. In that case the equation is:
x[(r7 + log2(w)) : r7] = (r6 ^ r7),
In the function r7 = rot_const, seq = (r6 ^ r7) and seq_len is the bit length of seq. In RC5 seq_len is log2(word_size).
| x | value |
| rot_const | r7 |
| bit_seq | bit sequence that will be matched against seq_len bits rotated by rot_const in x . Example: r6 ^ r7 . |
| bit_seq_len | length of the sequence of bits that is checked if it matches the same length of bits in x |
| bool rc5_last_round_eq_x_bit_seq_match_bitwise | ( | const WORD_T | x, |
| const uint32_t | rot_const, | ||
| const WORD_T | bit_seq, | ||
| const uint32_t | bit_seq_len | ||
| ) |
Wrapper for rc5_last_round_eq_x_bit_seq_match_bit_i . Returns false only if any of the required bits don't match. Otherwise returns true.
For Rc5: x = value, rot_const = r7, bit_seq = r6^r7, bit_seq_len = log2(w)
| bool rc5_last_round_eq_x_find_solutions_rec | ( | const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2], |
| const eq_x_params_t | eq_params, | ||
| std::vector< WORD_T > * | sol_vec | ||
| ) |
Wrapper for rc5_last_round_eq_x_find_solutions_rec_i
| A | transition matrix A[x[i]]|[y[i]][yy[i]][dx[i]] |
| bool rc5_last_round_eq_x_has_solution | ( | const uint32_t | i, |
| const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2], | ||
| const gsl_vector * | L, | ||
| const gsl_vector * | C, | ||
| const eq_x_params_t | eq_params, | ||
| const WORD_T | x_sol, | ||
| WORD_T * | sol | ||
| ) |
Check if there is at least one solution x that satisfies the equation: 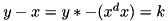 where y, y* and dx are fixed.
where y, y* and dx are fixed.
| A | transition matrix AA[x[i]]|[y[i]][yy[i]][dx[i]] |
| void rc5_last_round_eq_x_sf | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2] | ) |
Construct the transition matrices for counting the number of solutions x of the equation from the last round of RC5:
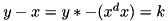
for fixed y, y* and dx.
| A[x[i]][y[i]][y*[i]][dx[i]] | zero-initialized set of matrices |
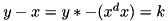 .
.![$A[2][2][2][2] = A[x[i]][y[i]][yy[i]][dx[i]]$](form_306.png) , where
, where
![$y[i]$](form_303.png) : the i-th bit of the first output value.
: the i-th bit of the first output value.![$yy[i]$](form_307.png) : the i-th bit of the second output value.
: the i-th bit of the second output value.![$dx[i]$](form_308.png) : the i-th bit of the input difference.
: the i-th bit of the input difference.The same matrices can also be used for counting the number of solutions y of the equation from the FIRST round of RC5:
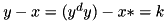
for fixed x, x* and dy, where x and x* are the chosen plaintexts satisfying a fixed input difference dx = x ^ x*.
When used for the FIRST round the meaning of the dimensions of the A matrices is: A[y][x][xx][dy] (as opposed to A[x][y][yy][dx] for the FIRST round).
LAST round: A[x][y][yy][dx] : LAST round (y, yy, dx - fixed) FIRST round: A[y][x][xx][dy] : FIRST round (x, xx, dy - fixed)
| void rc5_mid_round_eq_add_matrices | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2], |
| gsl_matrix * | AA[2][2][2][2] | ||
| ) |
RC5 middle round: compute A from AA where
AA[2][2][2][2] = AA[y[i]][x[i]][dy[i]][dx[i]]
A[2][2] = A[dy[i]][dx[i]] = {(i,j)} AA[i][j][dy[i]][dx[i]]
| void rc5_mid_round_eq_alloc_matrices_4d | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2] | ) |
Allocate memory for the mid round equation of RC5
| void rc5_mid_round_eq_free_matrices_4d | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2] | ) |
Free memory reserved by a previous call to rc5_mid_round_eq_alloc_matrices .
| void rc5_mid_round_eq_print_matrices | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2] | ) |
Print the matrices for mid round eq. of RC5.
| bool rc5_mid_round_eq_xy_find_solutions_exper | ( | const WORD_T | dy, |
| const WORD_T | dx, | ||
| std::vector< WORD_T > * | sol_vec | ||
| ) |
Experimentally list all solutions (x,y) of the equation:
y - x = (y ^ dy) - (x ^ dx) (= k)
| void rc5_mid_round_eq_xy_sf | ( | gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2][2] | ) |
Construct the transition matrices for counting the number of solutions (x,y) of the equation from a middle round of RC5:
y - x = (y^dy) - (x^dx) (= k) .
for fixed dy, dx.
| A[x[i]][y[i]][dy[i]][dx[i]] | zero-initialized set of matrices |
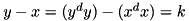 .
.![$A[2][2][2][2] = A[y[i]][x[i]][dy[i]][dx[i]]$](form_311.png) , where
, where
![$x[i]$](form_312.png) : the i-th bit of the output value.
: the i-th bit of the output value.![$y[i]$](form_303.png) : the i-th bit of the input value.
: the i-th bit of the input value.![$dx[i]$](form_308.png) : the i-th bit of the output difference.
: the i-th bit of the output difference.![$dy[i]$](form_313.png) : the i-th bit of the input difference.
: the i-th bit of the input difference.| double rc5_xdp_add_first_round_exper | ( | WORD_T | x, |
| WORD_T | xx, | ||
| WORD_T | dy | ||
| ) |
Experimental computation of the probability:
xdp^{+}_FR(x, xx -> dy) over all keys)
| double rc5_xdp_add_last_round | ( | const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2], |
| const gsl_vector * | L, | ||
| const gsl_vector * | C, | ||
| const WORD_T | y, | ||
| const WORD_T | yy, | ||
| const WORD_T | dx | ||
| ) |
Theoretical computation of the probability:
xdp^{+}_LR(y, yy -> dx) over all keys)
Counts the number of solutions x to the equation:
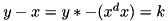
where y, y* and dx are fixed.
A[y[i]][yy[i]][dx[i]]
xdp^{+}_FR(x, xx -> dy) over all keys)
Counts the number of solutions y to the equation:
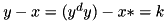
where x, x* and dy are fixed.
A[x[i]][xx[i]][dy[i]]
| void rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out | ( | const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2], |
| const gsl_vector * | L, | ||
| const gsl_vector * | C, | ||
| const WORD_T | y, | ||
| const WORD_T | yy, | ||
| const WORD_T | dx_prev, | ||
| const uint32_t | rot_const_prev, | ||
| const double | p_thres, | ||
| const uint32_t | hw_thres, | ||
| std::vector< WORD_T > * | dx_vec | ||
| ) |
Wrapper for rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out_i . Same as rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out but with pre-computed matrices.
| dx_prev | the left ciphertext rotated right by the last rot const |
| rot_const_prev | the last rot const |
| void rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out_i | ( | const uint32_t | i, |
| const double | p_thres, | ||
| const uint32_t | hw_thres, | ||
| const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2][2], | ||
| const gsl_vector * | L, | ||
| const gsl_vector * | C, | ||
| const WORD_T | y, | ||
| const WORD_T | yy, | ||
| const WORD_T | dx_prev, | ||
| const uint32_t | rot_const_prev, | ||
| const WORD_T | dx, | ||
| const double | p, | ||
| std::vector< WORD_T > * | dx_vec | ||
| ) |
For fixed y,yy generate all output differences dx for which the probability xdp^{+}_LR(y, yy -> dx) over all keys is above a certain threshold.
rot_const_next_vec_2d contains a list of possible rot constants for every difference in dx_vec
Check if a sequence of log2(n) bits of dx starting from position rot_const_prev is equal to the 0 bit sequence. This check is relevant only for RC5 and is related to the equal rotation constant requirement.
| void rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out_wrapper | ( | const WORD_T | y, |
| const WORD_T | yy, | ||
| const double | p_thres, | ||
| std::vector< WORD_T > * | dx_vec | ||
| ) |
Wrapper for rc5_xdp_add_last_round_diff_set_out_i .
| double rc5_xdp_add_last_round_exper | ( | WORD_T | y, |
| WORD_T | yy, | ||
| WORD_T | dx | ||
| ) |
Experimental computation of the probability:
xdp^{+}_LR(y, yy -> dx) over all keys)
| double rc5_xdp_add_mid_round | ( | const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2], |
| const gsl_vector * | L, | ||
| const gsl_vector * | C, | ||
| const WORD_T | dy, | ||
| const WORD_T | dx | ||
| ) |
Theoretical computation of the probability:
xdp^{+}_MR(dy -> dx) over all tuples (x,y)
It counts the number of solutions (x,y) s.t.:
y - x = (y ^ dy) - (x ^ dx) (= k) for fixed dx, dy
| void rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out | ( | const gsl_matrix * | A[2][2], |
| const gsl_vector * | L, | ||
| const gsl_vector * | C, | ||
| const WORD_T | dy, | ||
| const WORD_T | dx_prev, | ||
| const uint32_t | rot_const_prev, | ||
| const double | p_thres, | ||
| const WORD_T | hw_thres, | ||
| std::vector< WORD_T > * | dx_vec | ||
| ) |
Wrapper for rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out_i . Same as rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out but with pre-computed matrices.
| void rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out | ( | const WORD_T | dy, |
| const WORD_T | dx_prev, | ||
| const WORD_T | rot_const_prev, | ||
| const double | p_thres, | ||
| const uint32_t | hw_thres, | ||
| std::vector< WORD_T > * | dx_vec | ||
| ) |
Wrapper for rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out_i .
| void rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_diff_set_out_exper | ( | const WORD_T | dy, |
| const double | p_thres, | ||
| std::vector< WORD_T > * | dx_vec | ||
| ) |
Experimentally generate all dx s.t. xdp^{+}_MR(dy -> dx) > p_thres
| double rc5_xdp_add_mid_round_exper | ( | const WORD_T | dy, |
| const WORD_T | dx | ||
| ) |
Experimental computation of the probability:
xdp^{+}_MR(dy -> dx) over all tuples (x,y)
It counts the number of solutions (x,y) s.t.:
y - x = (y ^ dy) - (x ^ dx) (= k)